In this article we will look at two common measures of English proficiency: the Common European Framework of Reference for Languages (CEFR) and the International English Language Test System (IELTS) and how to convert your CEFR Level to IELTS. One of the most important things for any foreign language student is to achieve a certain level of proficiency, whether it is to be accepted at a university, getting a job or obtaining a certificate.
The CEFR is one of the most commonly used measures of students’ foreign language abilities. However, there are several other tests and measures for English as a Second Language, including the IELTS. In this article, we will discuss how to convert your IELTS scores into CEFR levels, what each level means and how this can be useful for your exam preparation.
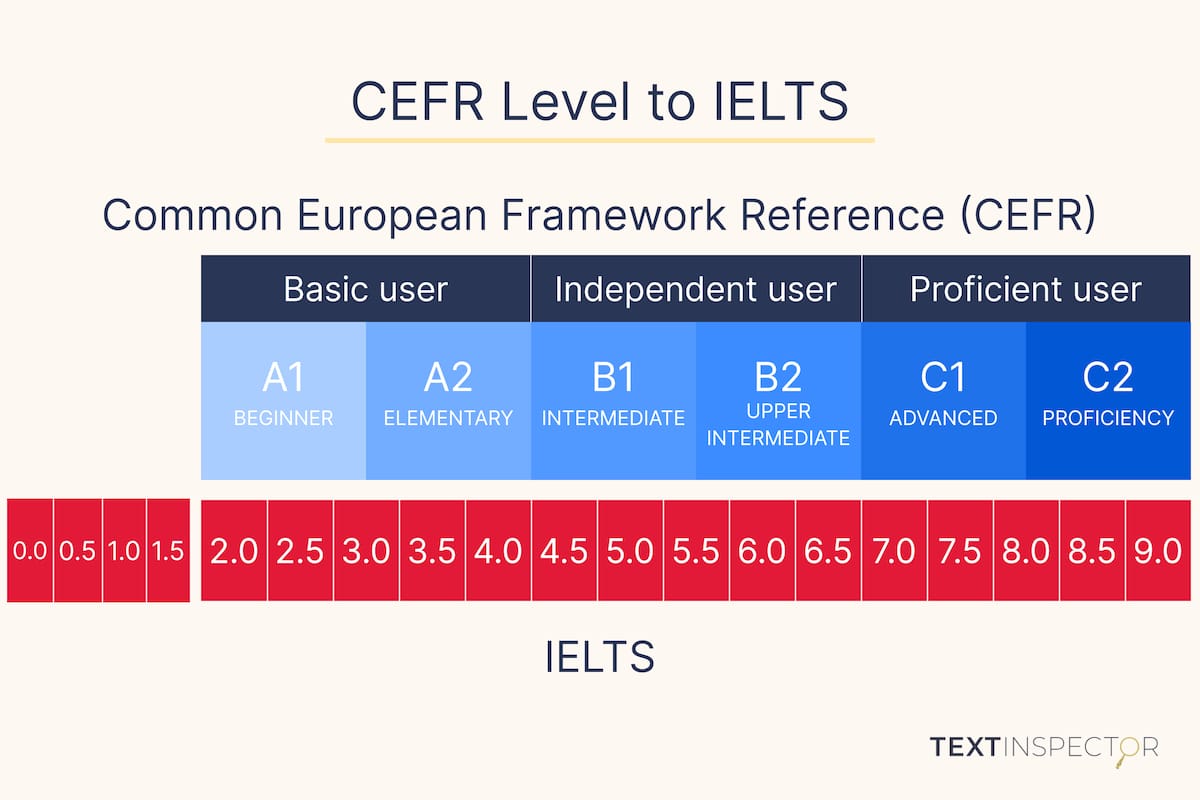
CEFR Level to IELTS score comparison
The table below can be used as an IELTS to CEFR level calculator:
| CEFR Level | Language Proficiency Level | Corresponding IELTS Band Score |
C2 | Expert User | 9.0 |
| 8.5 | ||
C1 | Very Good User | 8.0 |
Good User | 7.5 | |
| 7.0 | ||
B2 | Competent User | 6.5 |
| 6.0 | ||
Modest User | 5.5 | |
| 5.0 | ||
B1 | Limited User | 4.5 |
| 4.0 | ||
A2 | Extremely Limited User | 3.5 |
| 3.0 | ||
A1 | Intermittent User | 2.5 |
| 2.0 | ||
N/A | Non-user | 1.5 |
| 1.0 | ||
N/A | Did not attempt test | 0.5 |
| 0.0 |
Using this table as an IELTS to CEFR calculator can help you establish clear goals when preparing to sit for this test, taking into account the requirements that the university or country visa you would like to apply for has. In this way, you can get an idea of the level of proficiency you need to reach, enabling you to take control of your education and work prospects.
What is the CEFR?
The Council of Europe began specifying “threshold levels” for English and French in the mid-1970s. As part of this, the CEFR was released in 2001 and became a landmark for foreign language teaching, for it provided a substantial structure to describe different levels of proficiency, and it was adaptable to suit different languages.
Some of its other objectives were to promote language diversification, to develop language curricula and textbooks to improve quality and success in the learning, teaching and assessment processes, to ensure transparency and to empower teachers. It also helped promote new methodologies such as the communicative approach.
Language proficiency is organised in six levels, A1 to C2, which can be categorised into three broad levels: Basic User (A1, A2), Independent User (B1, B2) and Proficient User (C1, C2). which can be further subdivided.
The CEFR language levels are defined through ‘can-do’ descriptors that help categorise foreign language learners’ proficiency as follows:
CEFR Level A1: a basic user who can understand and use simple terms, identify themselves and provide or ask for personal information, and can discuss everyday topics.
CEFR Level A2: a basic user who can comprehend commonly used phrases and expressions in daily contexts like work or shopping; can also give simple directions and discuss wishes and needs.
CEFR Level B1: an independent user who can comprehend and talk about family, friends, work or free time activities, and can discuss travel needs or write short paragraphs based on interests, aspirations and experiences.
CEFR Level B2: an independent user able to write documents about different topics, comprehend important concepts using complicated texts and discuss naturally with native speakers.
CEFR Level C1: a proficient user who can understand complex discussions or messages, can explain difficult concepts in professional, social or formal situations, and can write detailed texts about in-depth subjects.
CEFR Level C2: a proficient user able to understand virtually everything heard or read, summarise information from different sources, and express themself spontaneously, very fluently and precisely.
What is IELTS?
Created in the 1980s, the IELTS (short for International English Language Test System) is an international standardised test that has four sections: Listening, Reading, Writing and Speaking. Non-native English speakers can take this test in order to certify their mastery of the language.
Sitting for the IELTS can help you study abroad, get a visa, or land a job. IELTS is widely accepted all over the world as a proof of your proficiency in English. Scores obtained out of 40 are converted to the band scale of 0 (zero) to 9 (nine). It is crucial to know which band score you are required to achieve so as to apply to a university or for a visa.
Your IELTS test results will show both an overall test score of between 0 and 9, as well as individual scores for each section of the exam. This scale helps you understand your level of English and what you can do with it. Here are the 9 band scores of IELTS explained:
9 Skill Level: Expert
- The test taker has fully operational command of the language.
- Their use of English is appropriate, accurate and fluent, and shows complete understanding.
8 Skill Level: Very good
- The test taker has fully operational command of the language with only occasional unsystematic inaccuracies and inappropriate usage.
- They may misunderstand some things in unfamiliar situations. They handle complex and detailed argumentation well.
7 Skill Level: Good
- The test taker has operational command of the language, though with occasional inaccuracies, inappropriate usage and misunderstandings in some situations.
- They generally handle complex language well and understand detailed reasoning.
6 Skill Level: Competent
- The test taker has an effective command of the language despite some inaccuracies, inappropriate usage and misunderstandings.
- They can use and understand reasonably complex language, particularly in familiar situations.
5 Skill Level: Modest
- The test taker has a partial command of the language and copes with overall meaning in most situations, although they are likely to make many mistakes.
- They should be able to handle basic communication in their own field.
4 Skill Level: Limited
- The test taker’s basic competence is limited to familiar situations.
- They frequently show problems in understanding and expression.
3 Skill Level: Extremely limited
- The test taker conveys and understands only general meaning in very familiar situations.
- There are frequent breakdowns in communication.
2 Skill Level: Intermittent
- The test taker has great difficulty understanding spoken and written English.
1 Skill Level: Non-user
- The test taker has no ability to use the language except a few isolated words.
0 Skill Level: Did not attempt the test
- The test taker did not answer the questions.
Why compare your CEFR Level to IELTS?
If you would like to study at an English-speaking university, it is important to be aware of its language requirements and to be able to compare the CEFR level to IELTS scores. The CEFR levels are standardised to determine your fluency in English and they are easier to understand than the IELTS bands. In addition, some companies and organisations might prefer using CEFR levels.
The CEFR level and IELTS scores comparison gets rid of confusing terms such as “Basic,” “Intermediate,” and “Advanced” and provides more accurate indicators. Cambridge Assessment has mapped the correlation between CEFR levels and IELTS scores to help candidates better understand their results.
Current research and improvements
Cambridge Assessment has carried out many studies to help students understand the relationship between the IELTS scores and the CEFR level. Since IELTS is not a level-based test, but one designed to encompass a broader proficiency continuum, establishing a one-to-one correspondence between IELTS scores and CEFR levels is not easy, and may need to be revised accordingly as time passes.
It is also important to remember that IELTS band scores are overall band scores, not the individual band scores for Listening, Reading, Writing, and Speaking. As the CEFR becomes more prominent in how institutions assess language requirements, how to interpret IELTS scores in CEFR terms is an essential tool for students.
Whether you are looking to get into a university, apply for a visa, or start a professional career, being able to compare your CEFR Level to IELTS will help you decide how much work you need to put in to pass your exams. Knowing your objectives with certainty is the best way to fulfil your dreams!
References
- Badoni, A., & Chadha, D. (2023, November 20). C1 Level English | Know Its Comparison with IELTS Score! iSchoolPrep. Retrieved December 16, 2023, from https://ischoolprep.com/blog/what-is-c1-level-english-ielts-score/
- Comparing scores to IELTS. (n.d.). Cambridge English. Retrieved December 14, 2023, from
https://www.cambridgeenglish.org/images/461626-cambridge-english-qualifications-comparing-scores-to-ielts.pdf - IELTS and the CEFR. (n.d.). IELTS. Retrieved December 14, 2023, from https://ielts.org/organisations/ielts-for-organisations/compare-ielts/ielts-and-the-cefr
- Understand CEFR Level in IELTS: A Score Comparison. (n.d.). Kanan International. Retrieved December 15, 2023, from https://www.kanan.co/blog/cefr-level-ielts/#how-to-compare-cefr-with-ielts-scores
Contributed by Victoria Martínez Mutri
Victoria is a CELTA-certified English as a Foreign Language teacher, with a background in Translation, from Buenos Aires, Argentina. Fascinated by language since an early age, she’s particularly interested in the fields of Applied Linguistics and Sociolinguistics. She’s been researching and writing about gender-inclusive language since 2018. After graduating, she would like to obtain a Master’s Degree in Linguistics at a foreign university.
Share
Related Posts

An Easy Recipe To Prepare ESL Content
6 February, 2024
Have you ever compared yourself to a chef as an ESL teacher? It might sound strange, but there’s more in common than you might think. Like a chef, you carefully choose and mix words and ideas to prepare lessons that will help your students grow their language skills. Your students are like diners, ready to enjoy the meal you’ve cooked up in your classroom kitchen.
Today we will be discussing quick methods to help you prepare ESL content. As a language teaching expert, while it may not seem obvious at first, you share similarities with professional chefs. Think about it – you value precision and carefully weigh every word you use to create effective reading material for language learners, ensuring every morsel of content they consume boosts their language skills.
Read More ->
Inclusivity in Teaching English: 4 Reasons Why It Matters & How to Improve It Instantly
25 September, 2023
An ideal ESL teaching scenario creates a space where everyone gets equal opportunities to learn and thrive, where students, regardless of where they’re from, feel like they belong, and where language education becomes a powerful tool to build competence and confidence among the leaders of tomorrow. This is precisely what inclusivity in teaching can do.
Read More ->
Difference Between ESL and EFL: Same Language, Different Worlds
11 August, 2025
English is taught and learned all over the world, but the context in which it’s […]
Read More ->